
Parent table (Referenced table) has a primary key, and foreign key (referencing table) is used in the second table to create a connection with parent table.ġ) We cannot delete any row from the primary table (Referenced table) if the same row is available in referencing table.
A foreign key is used to create a connection between two tables. Referential Integrity: Referential integrity concern with the concept foreign key. Each primary key column contains a value, but not contain a NULL value. It also checks for the Null value according to integrity check.Įntity Integrity: Rules state that primary key should be applied to a column or sets of the column to store unique values in a tuple. There are four data integrity checks.ĭomain Integrity: It specifies that attribute must contain the data item according to defined data type, the range of an attribute during relation creation. To bring consistency and assure the security of data many integrity checks applied on the table. It integrates the whole data and makes it complete. Data Integrity Rulesĭata Integrity rules assure that data is consistent and unique in a table. NULL and zero ‘0’ both are different from each other.

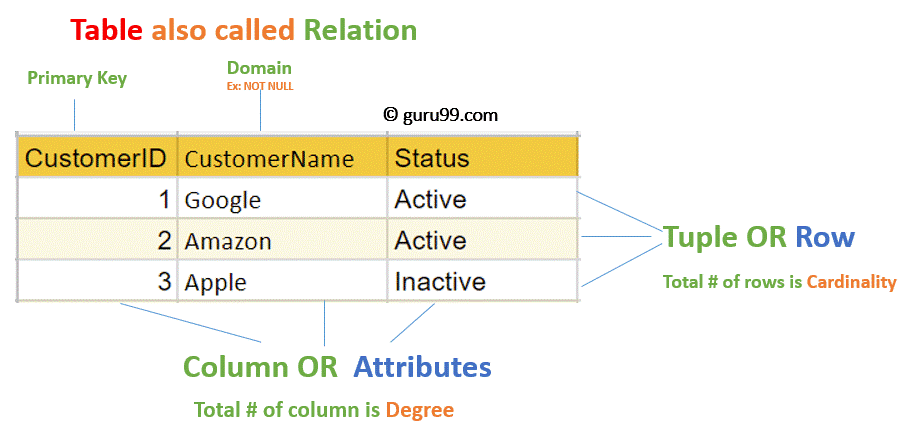
NULL is a particular value of tuple.For example in Student table entry, if he /she is living with guardian than parents attribute has a NULL value or if he/she is living with parents than guardian attribute has a NULL value. NULL is used to represent not applied data values of the tuple in a table. Degrees of a relation represents the number of the attribute (columns) in a relation. It specifies that attribute has aninteger value, char value, etc. Domains specify the specific values for an attribute. In a relational database, a row is called a tuple and a column header is known as an attribute like ”student_name,” ”Class” and the table is called a relation. In addition, the book looks at the impact of big data on relational databases and the option of using NoSQL databases for that purpose.In relational model data stored in cells of a table having a unique key to identify or access the data without any redundancy and duplicity. Topics such as the relational data model, normalization, data entities, and Codd's Rules (and why they are important) are covered clearly and concisely. The book begins by reviewing basic concepts of databases and database design, then turns to creating, populating, and retrieving data using SQL. This book covers relational database theory as well as providing a solid introduction to SQL, the international standard for the relational database data manipulation language. Most of those in use today are based on the relational data model, a way of representing data and data relationships using only two-dimensional tables. Relational Database Design and Implementation: Clearly Explained, Fourth Edition, provides the conceptual and practical information necessary to develop a database design and management scheme that ensures data accuracy and user satisfaction while optimizing performance.ĭatabase systems underlie the large majority of business information systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
